2023-04-18:论文速递
1、DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision
自监督 + 无需微调
《DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision》
URL:https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.07193
Official Code:https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2
单位:MetaAI
Demo:https://dinov2.metademolab.com/demos
DINOv2: A Self-supervised Vision Transformer Model
A family of foundation models producing universal features suitable for image-level visual tasks (image classification, instance retrieval, video understanding) as well as pixel-level visual tasks (depth estimation, semantic segmentation).
一种基础模型,产生适用于图像级视觉任务(图像分类、实例检索、视频理解)以及像素级视觉任务(深度估计、语义分割)的通用特征
the first method for training computer vision models that uses self-supervised learning to achieve results that match or surpass the standard approach used in the field
DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features Without Supervision
A family of models to encode visual features, evaluated across 30 different benchmarks covering 8 types of visual tasks from image classification to monocular depth estimation.
一种用于编码视觉特征的模型,通过 30 个不同的基准进行评估,涵盖从图像分类到单目深度估计的 8 种视觉任务
前言
继 SAM 之后,MetaAI 在 CV 领域又一重量级开源项目:DINOv2。
小扎也是高调表示,Meta 一直致力于开源各种 AI 工具,而今天发布的 DINOv2 更是 SOTA 级别的模型。能在深度估计、语义分割、图像相似性比较等方面实现自监督训练。
小扎还表示,用这个模型可以借助卫星图像生成不同大洲的森林高度。而在未来,还可以帮助医学成像、粮食产量等方面。
当然,最后小扎还不忘了自己的主打——元宇宙。他认为,DINOv2 可以极大地加持元宇宙的建设,让用户在元宇宙中的沉浸体验更出色。
DINOv2 模型是在没有监督的情况下对包含 1.42 亿张图像的大型、精选和多样化数据集进行预训练的
DINOv2 系列模型在自我监督学习 (SSL) 方面比之前的最新技术有了显着改进,并达到了与弱监督特征 (WSL) 相当的性能
DINOv2 模型表现出强大的分布外性能,并且生成的特征无需任何微调即可使用
摘要
The recent breakthroughs in natural language processing for model pretraining on large quantities of data have opened the way for similar foundation models in computer vision. These models could greatly simplify the use of images in any system by producing all-purpose visual features, i.e., features that work across image distributions and tasks without finetuning. This work shows that existing pretraining methods, especially self-supervised methods, can produce such features if trained on enough curated data from diverse sources. We revisit existing approaches and combine different techniques to scale our pretraining in terms of data and model size. Most of the technical contributions aim at accelerating and stabilizing the training at scale. In terms of data, we propose an automatic pipeline to build a dedicated, diverse, and curated image dataset instead of uncurated data, as typically done in the self-supervised literature. In terms of models, we train a ViT model with 1B parameters and distill it into a series of smaller models that surpass the best available all-purpose features, OpenCLIP on most of the benchmarks at image and pixel levels.
最近在对大量数据进行模型预训练的自然语言处理方面取得的突破为计算机视觉中类似的基础模型开辟了道路。这些模型可以通过生成 通用的视觉特征,即 无需微调 即可跨图像分布和任务工作的特征(迁移到其他任务),极大地简化图像在任何系统中的使用。这项工作表明,如果对来自不同来源的足够多的精选数据进行训练,现有的预训练方法,尤其是 自我监督方法,可以产生这样的特征。我们重新审视现有方法并结合不同的技术来扩展我们在数据和模型大小方面的预训练。大多数技术贡献旨在加速和稳定大规模培训。在数据方面,我们提出了一个 自动管道 来构建一个专用的、多样化的和精选的图像数据集,而不是像自我监督文献中通常所做的那样未经整理的数据。在模型方面,我们训练了一个具有 1B 参数的 ViT 模型,并将其 蒸馏 成一系列更小的模型,这些模型超越了最佳可用的通用功能,OpenCLIP 在图像和像素级别的大多数基准测试。
Demo 展示
DINOv2 的在线 Demo 无法处理 包含有正脸的图片,否则会出现下面的错误:
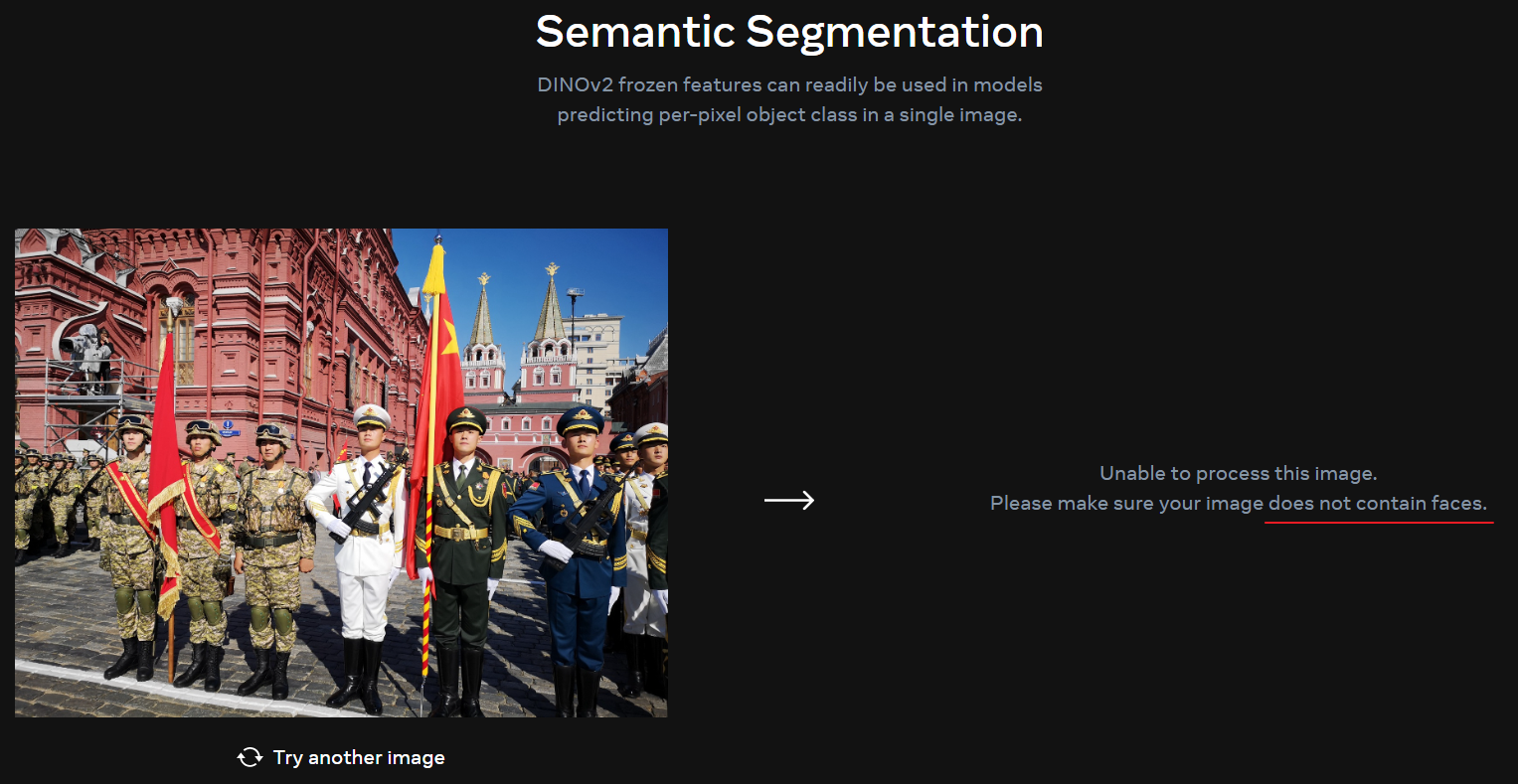
Semantic Segmentation(语义分割)
DINOv2 的语义分割结果如下所示:

详细的分割 Mask 图如下所示:

此外,也与 MetaAI 自家的 SAM 进行对比,其语义分割(使用 Everything 模式,没有使用额外的 Prompt)结果如下所示:
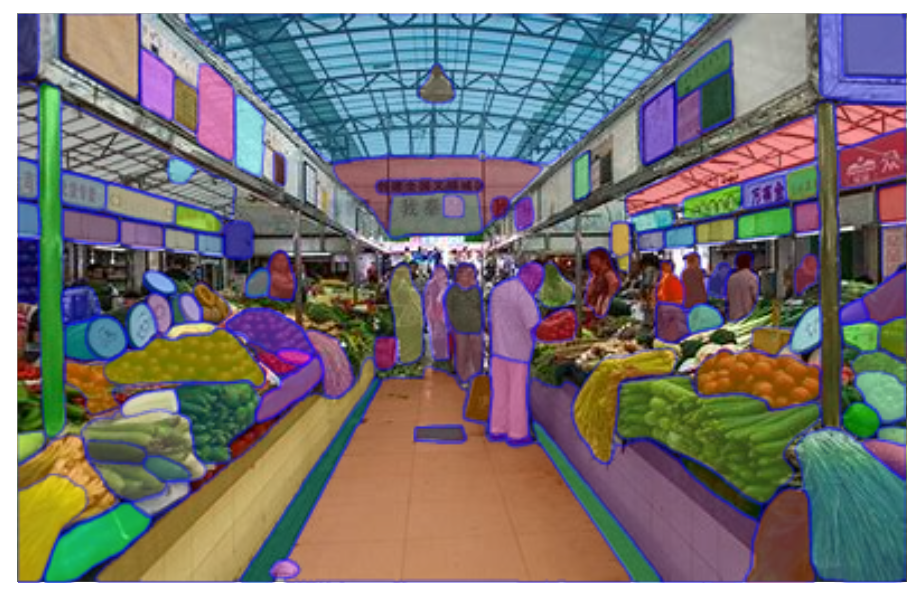

可以看出,相比 DINOv2,SAM 能够进行更细粒度(更多类别)的分割,而 DINOv2 主要对前景、背景等大片区域更敏感。
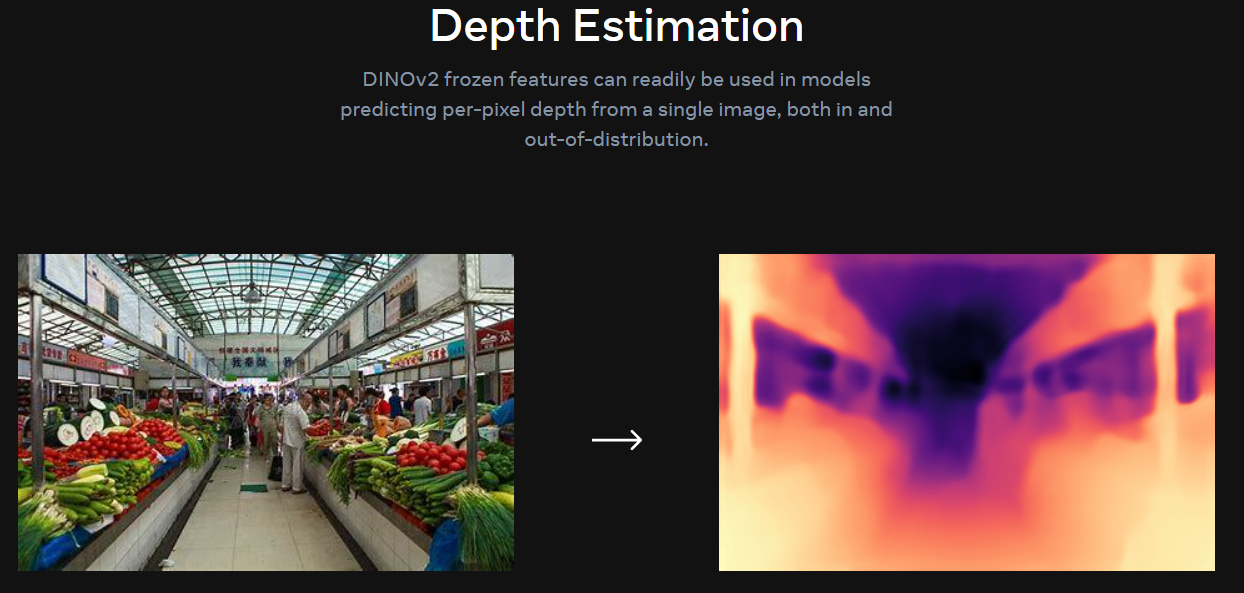
Depth Estimation(深度估计)
对于不熟悉计算机视觉的朋友来讲,深度估计(Depth Estimation) 可能是一个比较陌生的词汇。但其实,只要理解了其应用场景就能明白是什么意思了。
简单来说,对于 2D 照片,因为图像是一个平面,所以在 3D 重建 时,照片中 每一个点距离拍摄源的距离 就至关重要。 这就是深度估计的意义。
下面的图片中,相同的颜色代表距离拍摄点距离相同,颜色越浅距离越近。这样子整个图片的纵深就出来了。
Instance Retrieval(实例检索)
还是使用同样的菜市场图片,实例检索的部分结果如下图所示:
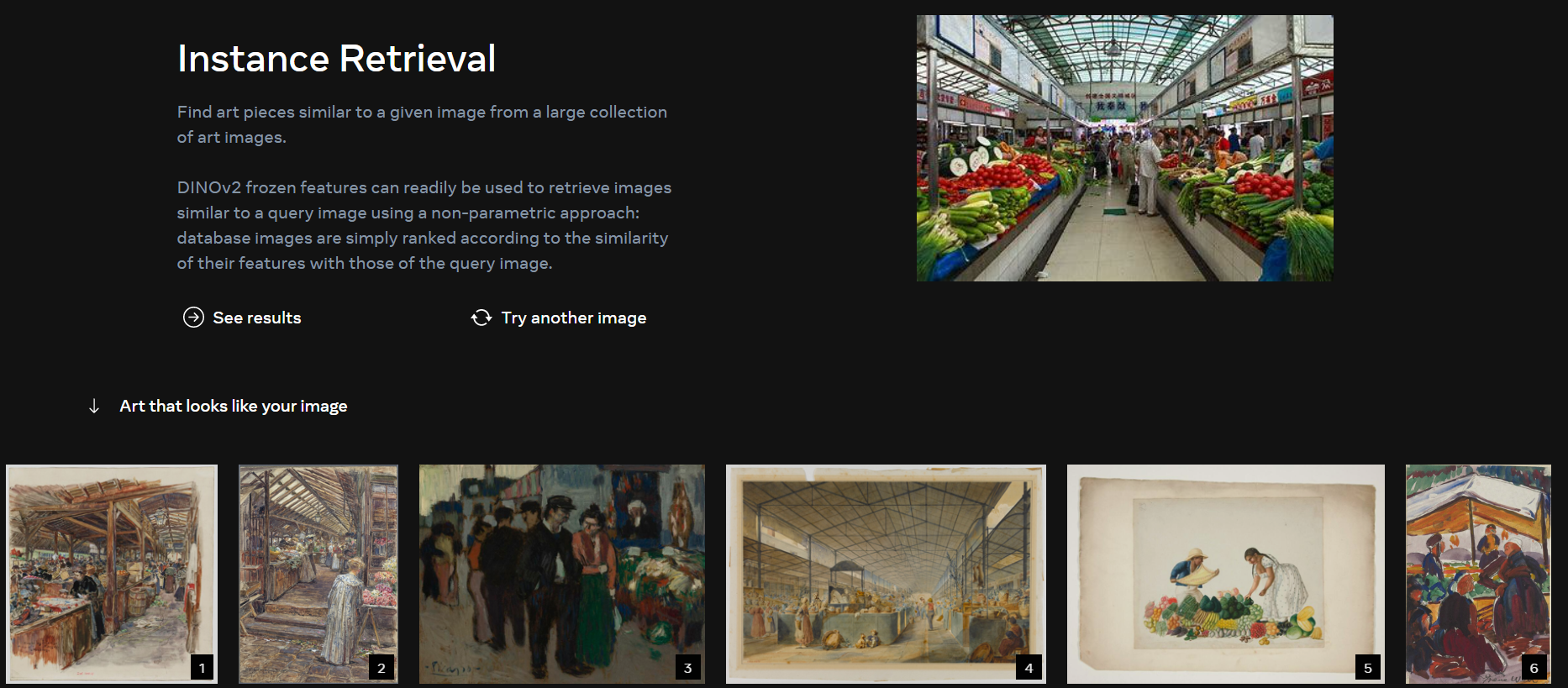
可以看出,检索出来的图片大部分还是符合 “菜市场” 这个场景。
篇幅所限,更多的演示结果可以参见 CV圈又炸了?小扎高调官宣DINOv2,分割检索无所不能,网友:Meta才是「Open」AI,也可以自己去 DINOv2 Demo 上进行体验。
具体方法
Data Pipeline
目标:构建大型(large)、精选(curated)且多样化(diverse)的数据集来训练模型。
为了提高性能,更大的模型需要更多的数据来训练,但是访问更多数据并不总是可能的。由于没有足够大的精选数据集满足需求,受 LASER 的启发,作者利用公开可用的爬虫数据库,构建了一个 数据处理管道(Data Process Pipeline) 来构建一个满足需求的数据集。
从这样的来源构建大规模预训练数据集需要两个关键要素:丢弃不相关 的图像和 跨概念 平衡数据集。
如此精细的管理实际上无法手动完成,我们需要一种方法来捕获不易与元数据相关联的分布。这是通过从大约 25 个第三方数据集 的集合中策划一组 种子图像(精选图像,Curated Data) 并通过检索足够接近这些种子图像的图像来扩展它来实现的。如下图所示:
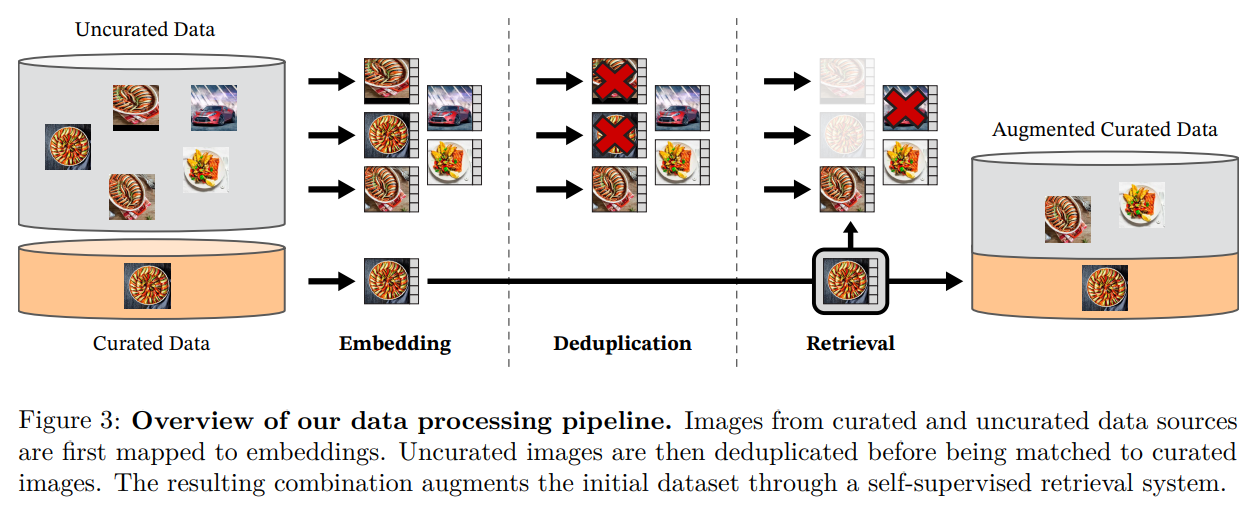
主要包括三个步骤:
来自精选和未精选数据源的图像首先映射到嵌入。然后,在与精选图像匹配之前,对未精选图像进行重复数据删除。由此产生的组合通过自我监督的检索系统扩充了初始数据集。
Embedding:将精选和未精选数据源中的图片进行 Embedding(嵌入)
Deduplicatio:删除 重复的 未精选图片(去重)
Retrieval:对未精选图片进行相似度检索,排除掉 不同类(不相似) 的图片(去异)
这种方法使我们能够从 12 亿张源图片中生成总计 1.42 亿张图片的预训练数据集。
DINOv2 的 Data Process Pipeline 其实与 SAM 中的 Data Engine 有 “异曲同工之妙”,这也表明:构建大的、高质量的、多样化的数据集非常重要。
实验结果

模型详情
作者提供了 4 个不同的模型,包括:DINOv2-S/B/L/g
1 ViT-g trained from scratch, and 3 ViT-S/B/L models distilled from the ViT-g.
The model takes an image as input and returns a class token and patch tokens.
The embedding dimension is:
384 for ViT-S
768 for ViT-B
1024 for ViT-L
1536 for ViT-g
The models follow a Transformer architecture, with a patch size of 14.
For a \(224\times 224\) image, this results in 1 class token + 256 patch tokens.
The models can accept larger images provided the image shapes are multiples of the patch size (14). If this condition is not verified, the model will crop to the closest smaller multiple of the patch size.
更多
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
LoRA 不太适合用来微调 VTG 这个任务?会将预测的输出几乎变为常数(变化很小)
# Meta-Net
# 参考 CoOpOp
self.meta_net = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("linear1", nn.Linear(vis_dim, vis_dim // 16)),
("relu", nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
("linear2", nn.Linear(vis_dim // 16, ctx_dim))
]))
# PromptLearner 的前向过程
def forward(self, im_features):
prefix = self.token_prefix
suffix = self.token_suffix
ctx = self.ctx # (n_ctx, ctx_dim)
bias = self.meta_net(im_features) # (batch, ctx_dim)
bias = bias.unsqueeze(1) # (batch, 1, ctx_dim)
ctx = ctx.unsqueeze(0) # (1, n_ctx, ctx_dim)
ctx_shifted = ctx + bias # (batch, n_ctx, ctx_dim)
# Use instance-conditioned context tokens for all classes
prompts = []
for ctx_shifted_i in ctx_shifted:
ctx_i = ctx_shifted_i.unsqueeze(0).expand(self.n_cls, -1, -1)
pts_i = self.construct_prompts(ctx_i, prefix, suffix) # (n_cls, n_tkn, ctx_dim)
prompts.append(pts_i)
prompts = torch.stack(prompts)
return prompts
参考
MetaAI Blog:DINOv2: State-of-the-art computer vision models with self-supervised learning
MetaAI DINOv2 Object:DINOv2: A Self-supervised Vision Transformer Model
文档信息
- 本文作者:Bookstall
- 本文链接:https://bookstall.github.io/wiki/2023-04-18-paper-list/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)