GPT-3 基本采用了 GPT-2 的结构,区别在于:
使用了更大的模型(更宽、更深)
使用了更多的训练数据
Few-shot、One-shot、Zero-shot 的训练方式(而不是微调)
使用了带状稀疏注意力(Spaned Sparse Attention)
with the exception that we use alternating dense and locally banded sparse attention patterns in the layers of the transformer, similar to the Sparse Transformer
对话 -> RAG(搜索增强生成)-> Tools -> GPTs
LLM 逆向诅咒
r GLM -> ChatGLM -> ChatGLM-2 -> ChatGLM-3
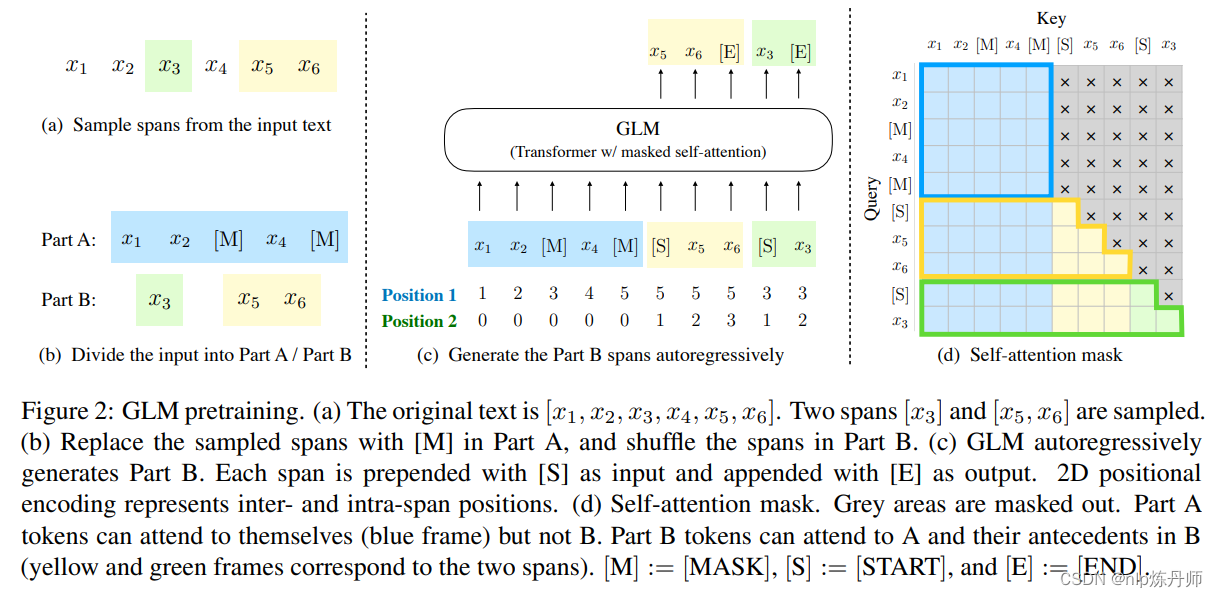
GLM
TODO
Autoregressive Blank Infilling
位置编码
2D 位置编码
ChatGLM-6B 代码中这一层采用的位置编码是 GLM 的中提出的 2D 位置编码
RoPE
ChatGLM-6B 相比标准的自注意力机制在 Q 和 K 中注入了 RoPE 位置信息。
"""
计算 cos m \theta_i 和 sin m \theta_i
"""
import torch
dim = 32
base = 10000
seq_len = 10
# 旋转角度
# 10000^(-2i / d) = 1 / (10000^(2i / d))
# i = [0, ...., d // 2] -> (dim // 2)
inv_freq = 1. / (base ** (torch.arange(0, dim, 2).float() / dim))
print(inv_freq.shape)
print("-----" * 10)
# Position m
# [0, ..., seq_len]
t = torch.arange(seq_len, dtype=inv_freq.dtype)
# 使用爱因斯坦求和函数 einsum 将 t 和 inv_freq 相乘,得到频率矩阵 freqs
# m * \theta -> (seq_len, dim // 2)
freqs = torch.einsum('i,j->ij', t, inv_freq)
print(freqs.shape)
print("-----" * 10)
# Different from paper, but it uses a different permutation in order to obtain the same calculation
# 通过在频率矩阵 freqs 中进行重复和拼接操作,生成旋转嵌入矩阵 emb,其维度为 [seq_len, dim]
# (seq_len, dim)
emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1)
print(emb.shape)
print("-----" * 10)
# 将旋转嵌入矩阵 emb 分别进行余弦和正弦运算
# [sx, 1 (b * np), hn]
cos_cached = emb.cos()[:, None, :] # (seq_len, 1, dim)
sin_cached = emb.sin()[:, None, :] # (seq_len, 1, dim)
print(cos_cached.shape, sin_cached.shape)
print("-----" * 10)
# 按照序列长度截取
cos_cached = cos_cached[:seq_len, ...] # (seq_len, 1, dim)
sin_cached = sin_cached[:seq_len, ...] # (seq_len, 1, dim)
print(cos_cached.shape, sin_cached.shape)
"""
构造 [q_0, q_1, ..., q_{dim // 2}] 和 [-q1, q0, -q3, q2, ....]
"""
def rotate_half(x):
x1, x2 = x[..., :x.shape[-1] // 2], x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2:]
return torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=x1.ndim - 1) # dim=-1 triggers a bug in earlier torch versions
"""
计算 q_0 * cos m \theta_0 + (-q_1) * sin m \theta_0
"""
@torch.jit.script
def apply_rotary_pos_emb_index(q, k, cos, sin, position_id):
# position_id: [sq, b], q, k: [sq, b, np, hn], cos: [sq, 1, hn] -> [sq, b, 1, hn]
cos, sin = F.embedding(position_id, cos.squeeze(1)).unsqueeze(2), \
F.embedding(position_id, sin.squeeze(1)).unsqueeze(2)
q, k = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin), (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)
return q, k
激活函数:GELU
@torch.jit.script
def gelu_impl(x):
"""OpenAI's gelu implementation."""
return 0.5 * x * (
1.0 + torch.tanh(0.7978845608028654 * x * (1.0 + 0.044715 * x * x))
)
def gelu(x):
return gelu_impl(x)
GLU 层
根据代码,GLU 可形式化表示为:
\[\text{GLU}(X) = \text{GELU}(X W_1) W_2\]参考
论文:
Github:GLM
文档信息
- 本文作者:Bookstall
- 本文链接:https://bookstall.github.io/2024/01/02/glm/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)