在提示学习(Prompt Learning)和提示微调(Prompt Tuning)领域,Prompt 集成算不算是一种数据增强技术?请一步一步进行思考,再给出详细的解释说明。
5 个 epoch 大概 1小时 -> 1 个 epoch 大约需要 12 分钟
Video Text Matching(VTM):视为一个 二分类问题
Concretely, for each video in a mini-batch, we randomly sample an unmatched text from the same batch to create an unpaired video-text input.
VIOLET:
VTM enhances the crossmodal fusion via modeling the alignments between visual and textual inputs.
At each training step, we randomly replace the corresponding text \(X_{pos}\) for a given video \(V\) with the text description \(X_{neg}\) from a different video in the same batch.
然后使用 Cross Entropy Loss: \(\begin{align} b_{pos}&=\text{FC}^{\text{VTM}}(h_{pos}^c) \\ b_{neg}&=\text{FC}^{\text{VTM}}(h_{neg}^c) \\ L_{VTM} &= -E[\log(b_{pso}) + \log(1-b_{neg})] \\ \end{align}\)
具体的 FC 结构如下所示:
import torch.nn as nn fc = nn.Sequential(*[ T.nn.Dropout(0.1), T.nn.Linear(768, 768*2), T.nn.ReLU(inplace=True), T.nn.Linear(768*2, 1) ])
All in One:
Given a paired video-text input, we randomly replace the paired video with a different video with the probability of 0.5 and ask the model to distinguish them. For the cls token of the last block, a single linear layer VTM head projects tokens to logits over binary class.
给定成对的视频文本输入,我们以 0.5 的概率(一半数量的正样本,一半负样本) 将成对的视频随机替换为不同的视频,并要求模型区分它们。对于最后一个 block 的 cls token,使用 单个线性层 VTM 头将令牌投射到二进制类上的 logits
使用 负对数似然(negative log-likelihood loss) 来计算 loss
具体的 Match Head 结构如下:
class vtmHead(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size): super().__init__() self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 2) def forward(self, x): x = self.fc(x) return x def init_weights(module): if isinstance(module, (nn.Linear, nn.Embedding)): module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=0.02) elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm): module.bias.data.zero_() module.weight.data.fill_(1.0) if isinstance(module, nn.Linear) and module.bias is not None: module.bias.data.zero_() vtm_score = vtmHead(hidden_size=768) vtm_score.apply(init_weights)
Prompt Tuning
peft’s prompt tuning
参考:https://github.com/huggingface/peft 的
src/peft/tuners/prompt_tuning.py
soft prompt tuning
参考:https://github.com/kipgparker/soft-prompt-tuning

定义 Soft Learnable Embedding:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class SoftEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
wte: nn.Embedding,
n_tokens: int = 10,
random_range: float = 0.5,
initialize_from_vocab: bool = True):
"""appends learned embedding to
Args:
wte (nn.Embedding): original transformer word embedding
n_tokens (int, optional): number of tokens for task. Defaults to 10.
random_range (float, optional): range to init embedding (if not initialize from vocab). Defaults to 0.5.
initialize_from_vocab (bool, optional): initalizes from default vocab. Defaults to True.
"""
super(SoftEmbedding, self).__init__()
self.wte = wte
self.n_tokens = n_tokens
self.learned_embedding = nn.parameter.Parameter(
self.initialize_embedding(wte,
n_tokens,
random_range,
initialize_from_vocab
)
)
def initialize_embedding(self,
wte: nn.Embedding,
n_tokens: int = 10,
random_range: float = 0.5,
initialize_from_vocab: bool = True):
"""initializes learned embedding
Args:
same as __init__
Returns:
torch.float: initialized using original schemes
"""
if initialize_from_vocab:
return self.wte.weight[:n_tokens].clone().detach()
return torch.FloatTensor(n_tokens, wte.weight.size(1)).uniform_(-random_range, random_range)
def forward(self, tokens):
"""run forward pass
Args:
tokens (torch.long): input tokens before encoding
Returns:
torch.float: encoding of text concatenated with learned task specifc embedding
"""
input_embedding = self.wte(tokens[:, self.n_tokens:])
learned_embedding = self.learned_embedding.repeat(input_embedding.size(0), 1, 1)
return torch.cat([learned_embedding, input_embedding], 1)
简单测试:
from transformers import GPT2LMHeadModel, GPT2TokenizerFast
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
n_tokens = 20 # 可学习的 token 长度
initialize_from_vocab = True # 使用预训练模型的 token embedding 进行初始化
tokenizer = GPT2TokenizerFast.from_pretrained("gpt2")
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained('gpt2')
s_wte = SoftEmbedding(
model.get_input_embeddings(),
n_tokens=n_tokens,
initialize_from_vocab=initialize_from_vocab
)
# 重新设置模型的 input embedding
model.set_input_embeddings(s_wte)
前向过程:
- 对于 soft prompt 的
input_ids,可以使用vocab_size - 1或者pad_token进行填充,还可以使用init_text对应的input_ids进行填充(例如 huggingfacepeft中对 prompt tuning 的定义)
inputs = tokenizer("May the force be", return_tensors="pt")
print(inputs['input_ids'].shape) # [1, 4]
print(inputs['attention_mask'].shape) # [1, 4]
# need to pad attention_mask and input_ids to be full seq_len + n_learned_tokens
# even though it does not matter what you pad input_ids with, it's just to make HF happy
inputs['input_ids'] = torch.cat([
torch.full((1, n_tokens), 50256), # 使用 50256 填充, 也可以使用 pad 等进行填充, 还可以使用 hard prompt 文本进行填充
inputs['input_ids']
], 1)
inputs['attention_mask'] = torch.cat([
torch.full((1,n_tokens), 1),
inputs['attention_mask']
], 1)
print(inputs['input_ids'].shape) # [1, 24]
print(inputs['attention_mask'].shape) # [1, 24]
outputs = model(**inputs)
print(outputs['logits'].shape) # [1, 24, 50257]
需要控制模型的梯度传播:
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if "learned_embedding" in name:
param.requires_grad = True
print(name)
# transformer.wte.learned_embedding : torch.Size([20, 768]) / True
else:
param.requires_grad = False
CVPR 2023:两行代码高效缓解视觉 Transformer 过拟合——DropKey
Prompt in Video Temporal Grounding
Pre-trained Image-Text Model
UNITER(开源模型权重)
Pre-trained Video-Text Model
VideoBERT(未开源模型权重)【2019】
UniVL【2020】
提供模型权重
《UniVL: A Unified Video and Language Pre-Training Model for Multimodal Understanding and Generation》
- URL:https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.06353
- Official Code:https://github.com/microsoft/UniVL
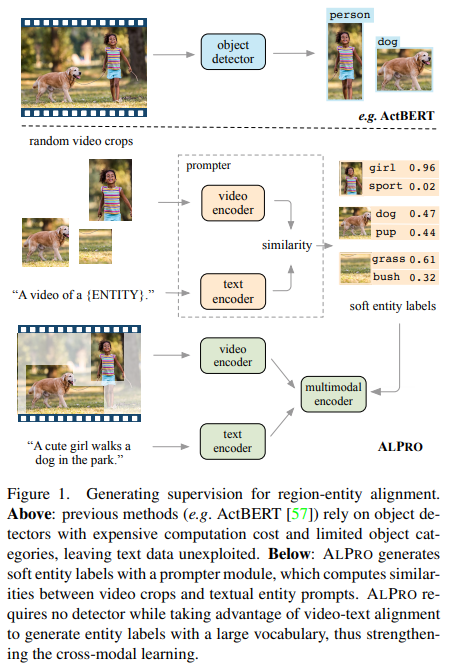
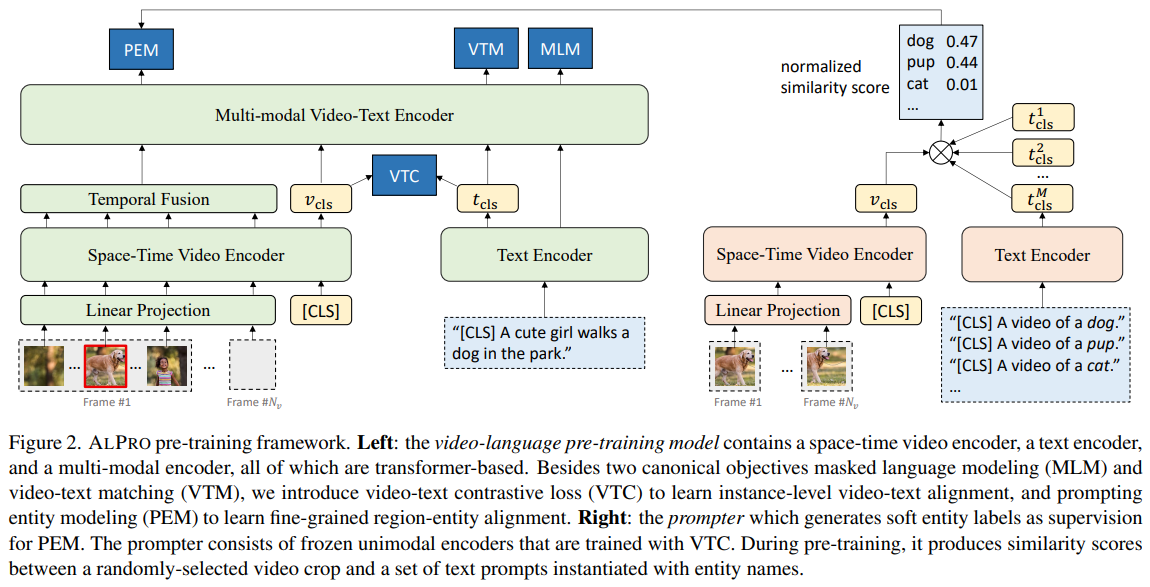
ALPRO【2021】
提供模型权重
《Align and Prompt: Video-and-Language Pre-training with Entity Prompts》
URL:https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.09583
会议:CVPR 2022
Official Code:https://github.com/salesforce/ALPRO
单位:Salesforce Research
VIOLET【2021】
提供模型权重

《VIOLET: End-to-End Video-Language Transformers with Masked Visual-token Modeling》
URL:https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.12681
单位:微软
Official Code:https://github.com/tsujuifu/pytorch_violet

SimVTP【2022】
提供模型权重
《SimVTP: Simple Video Text Pre-training with Masked Autoencoders》
- URL:https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.03490
Official Code:https://github.com/mayuelala/SimVTP

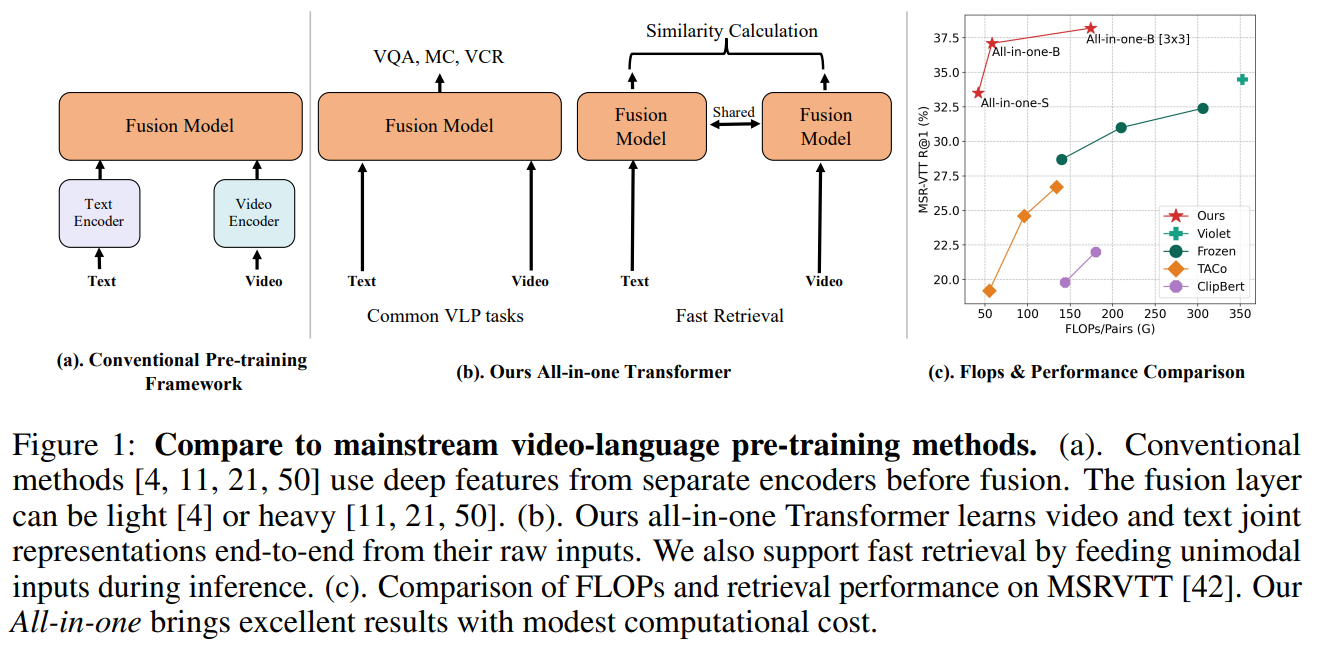
All in One【2022】
《All in One:Exploring Unified Video-Language Pre-training》
URL:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.07303
会议:CVPR 2023
Official Code:https://github.com/showlab/all-in-one
主流的 Video-Language 预训练模型(例如 ActBert、ClipBERT、VIOLET)由三部分组成,分别是:a video encoder, a text encoder, and a video-text fusion Transformer。
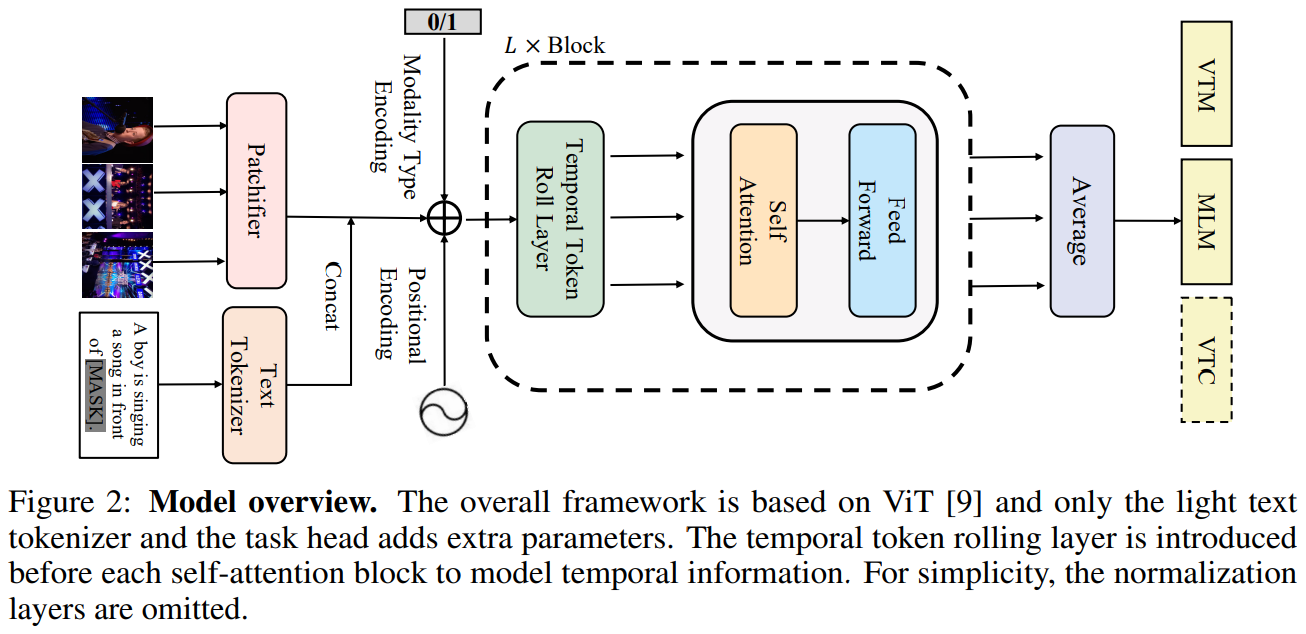
VIOLETv2【2023】
《An Empirical Study of End-to-End Video-Language Transformers with Masked Visual Modeling》
URL:
Official Code:https://github.com/tsujuifu/pytorch_empirical-mvm

TemPVL【2023】
《Temporal Perceiving Video-Language Pre-training》
URL:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.07463
单位:字节跳动、浙江大学
Official Code:暂时没有开源
TVG 数据集性能比较
下面的指标仅列出 R@1 的情况,而不考虑 R@5 的情况。
VLG-Net 论文中谈及了不使用 Charades-STA 数据集的原因
只取各方法原始论文中报道的实验结果
Charades-STA
| 模型\指标 | 年份 | 会议 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | - | - | 23.63 | 8.89 | - | ||
| ABLR | 2018 | AAAI 2019 | |||||
| ACL-K | 2018 | WACV 2019 | - | - | 30.48 | 12.20 | - |
| QSPN | - | 54.70 | 35.60 | 15.80 | - | ||
| TGN | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| MAN | - | - | 46.53 | 22.72 | - | ||
| SCDM | - | - | 54.44 | 33.43 | - | ||
| DEBUG | - | 54.95 | 37.39 | 17.69 | 36.34 | ||
| TSP-PRL | - | - | 37.39 | 17.69 | 37.22 | ||
| 2D-TAN (Pool) | 2019 | AAAI 2020 | - | - | 39.70 | 23.31 | - |
| 2D-TAN (Conv) | 2019 | AAAI 2020 | - | - | 39.81 | 23.25 | - |
| AVMR | 2020 | MM 2020 | 93.20 | 77.72 | 54.59 | - | - |
| VSLNet | 2020 | ACL 2020 | - | 64.30 | 47.31 | 30.19 | 45.15 |
| PLPNet (Phrase) | 2022 | - | 63.49 | 40.52 | 19.27 | 40.76 | |
| PLPNet(Sentence) | 2022 | - | 73.49 | 58.95 | 35.48 | 51.53 |
ActivityNet Captions
| 模型\指标 | 年份 | 会议 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCN | 21.36 | 6.43 | |||||
| CTRL | 29.01 | 10.34 | |||||
| ACRN | 31.67 | 11.25 | |||||
| ABLR | 2018 | AAAI 2019 | 73.30 | 55.67 | 36.79 | - | 36.99 |
| TGN | 27.93 | - | |||||
| CMIN | 44.62 | 24.48 | |||||
| 2D-TAN (Pool) | 2019 | AAAI 2020 | - | 59.45 | 44.51 | 26.54 | - |
| 2D-TAN (Conv) | 2019 | AAAI 2020 | - | 58.75 | 44.05 | 27.38 | - |
| CSMGAN | 2020 | MM 2020 | - | 68.52 | 49.11 | 29.15 | - |
| VSLNet | 2020 | ACL 2020 | - | 63.16 | 43.22 | 26.16 | 43.19 |
| VLG-Net | 2020 | - | - | 46.32 | 29.82 | - | |
| PLPNet (Phrase) | 2022 | - | 50.10 | 38.12 | 25.24 | 37.96 | |
| PLPNet (Sentence) | 2022 | - | 56.92 | 39.20 | 20.91 | 39.53 |
TACoS
根据 VSLNet 论文中对于 TACoS 数据集的描述,共有两种不同的形式:
- TACoS Origin:
- TACoS TAN:
TACoS origin
| 模型\指标 | 年份 | 会议 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCN | 2017 | ICCV 2017 | 14.42 | - | 5.58 | ||
| CTRL | 2017 | ICCV 2017 | 24.32 | 18.32 | 13.30 | - | - |
| ACRN | - | 19.52 | 14.62 | - | - | ||
| ABLR | 2018 | AAAI 2019 | 34.70 | 19.50 | 9.40 | - | 13.40 |
| ACL-K | 2018 | WACV 2019 | 31.64 | 24.17 | 20.01 | - | - |
| TGN | 41.87 | 21.77 | 18.90 | ||||
| MAN | - | - | - | ||||
| SCDM | - | 26.11 | 21.17 | - | |||
| QSPN | |||||||
| CSMGAM | 2020 | MM 2020 | 42.27 | 33.90 | 27.09 | - | - |
| 2D-TAN (Pool) | 2019 | AAAI 2020 | 47.59 | 37.29 | 25.32 | - | - |
| 2D-TAN (Conv) | 2019 | AAAI 2020 | 46.44 | 35.22 | 25.19 | - | - |
| DEBUG | - | 23.45 | 11.72 | - | 16.03 | ||
| AVMR | 2020 | MM 2020 | 89.77 | 72.16 | 49.13 | - | - |
| VSLNet | 2020 | ACL 2020 | - | 29.61 | 24.27 | 20.03 | 24.11 |
| VLG-Net | 2020 | 57.21 | 45.46 | 34.19 | - | - | |
大模型时代的建议
1、Give Up
2、Scale Up
Scale Down
Reuse and Remaster
fine tune 公开可用的预训练模型
5、Analysis
与公开可用的预训练模型有关的另一件事是分析它们。
6、RL, No Data
人们可能会降低对数据的要求,而是通过(在线)强化学习 (Reinforcement Learning, RL) 的视角来解决 AI 问题。
In fact, even the most efficient RL methods are known to be computationally heavy as the very process of exploration is costly. 但是,尽管是高效的 RL 方法,仍然需要昂贵的计算成本。
因此,底线(bottom line)是:如果你想摆脱对大型数据集的依赖,你可能还是需要大规模的算力,除非你处理的是比较简单的(toy)问题,或者是一些专门的领域(specialized domains)。
7、Small Models, No Compute
另一个有效的策略是在模型规模上做出妥协以节省计算量。在许多情况下,您想要或需要 更小的模型。考虑能够解决问题或完成任务的 最小模型,这对于现实世界的应用程序尤为重要,即 edge AI(边缘人工智能)。
Neuroevolution(神经进化) and neural architecture search(神经架构搜索), and knowledge distillation(知识蒸馏) methods are only a few of the available methods for edge AI. 这些方法只是 edge AI 的一部分。
此外,除了使用小的模型(small model)进行学习,还可以尝试从更少的数据(less data)中学习更多的知识。
8、Work on Specialized Application Areas or Domains
参考
文档信息
- 本文作者:Bookstall
- 本文链接:https://bookstall.github.io/2023/04/12/Prompt-VTG/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)