《Modular and Parameter-Efficient Multimodal Fusion with Prompting》
URL:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.08055
单位:慕尼黑大学(德国)
会议:ACL 2022
主页:https://aclanthology.org/2022.findings-acl.234/
Code:https://aclanthology.org/attachments/2022.findings-acl.234.software.zip
论文写的非常的清晰易懂、简洁又很详细!对初学者很友好!
Prompt 的两大优势:
高度模块化(high modularity)
让 Visual Encoder 专注于 Visual Representation 工作
让 Learnable Prompt Vectors 承担 模态对齐 任务
参数效率(Parameter Efficiency)
- 只需微调很少的参数,就能在 Few-Shot 场景下达到很高的性能
Prompting as Multimodal Fusing
前言
Recent research has made impressive progress in large-scale multimodal pre-training. In the context of the rapid growth of model size, it is necessary to seek efficient and flexible methods other than finetuning. In this paper, we propose to use prompt vectors to align the modalities. Our method achieves comparable performance to several other multimodal fusion methods in low-resource settings (Few-Shot or even Zero-Shot settings). We further show that our method is modular and parameter-efficient for processing tasks involving two or more data modalities.
整体结构
在 传统 Fine-Tuning 中 VE 的工作包括:
产生高质量的 Visual Representation 给 PLM
aligning the image and text spaces for a multimodal task
作者将 VE 的这两个工作进行 分解,并且将模态对齐的工作交由 Prompt Vectors 来做。
We randomly initialize \(N\) trainable vectors in the embedding layer of PLM. When processing downstream multimodal tasks, we finetune the prompt vectors but fix PLM and VE. 作者将这种方法称为 PromptFuse。
PromptFuse
PromptFuse 的整体结构如下图所示:
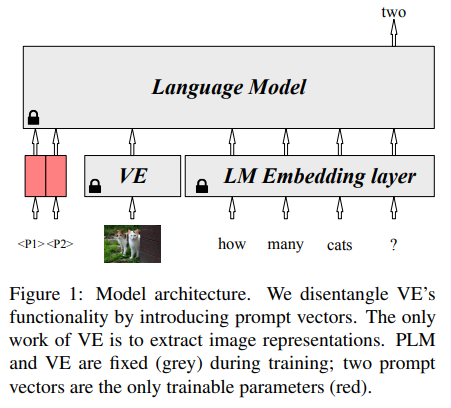
PromptFuse 的可训练参数很少,非常适合低资源环境(Few-Shot or Zero-Shot Settings)
BlindPrompt
作者为 PLM Encoder 设计了一种特殊的 Attention Mask,如下图所示:
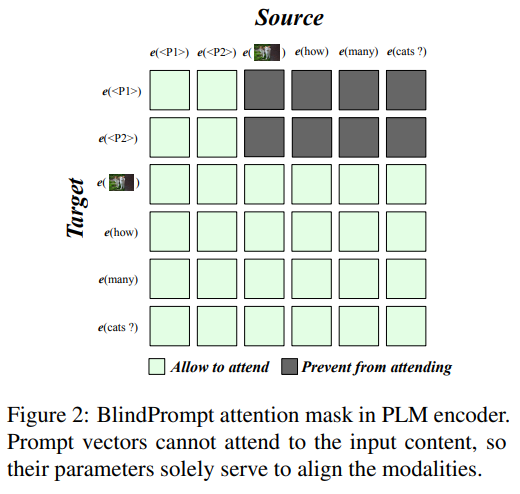
While the attention of input data remains fully visible, we enforce prompt vectors to only access each other but be blind to the input data. 这种 PromptFuse 的变体称为 BlindPrompt。
BlindPrompt 使用自注意层中的提示向量融合所有模态中的数据(但是 Prompt Vectors 并不能直接看到 Visual Data,只能看到 Text Data)。这进一步强调了提示向量应该关注模态之间的对齐,而不是模态内容的细节。
实验
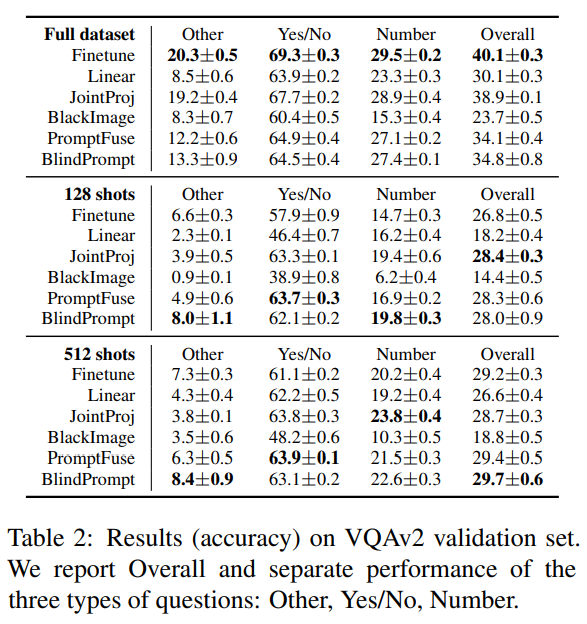
作者在两种模态(text、image)的 VQAv2 数据集和三种模态(text、video、audio)的 MUStARD 数据集上进行实验。
Baseline
We consider four baselines of fusing the modalities:
Finetune:finetune all-parameter in Visual Encoder (VE),使得 Visual Embedding Space 与 PLMs 的 Language Embedding Space 进行对齐
Linear:Fix VE,train a linear layer to projects the VE’s output
JointProj:将 Visual Embedding \(v\) 分别 concat 到句子中的每一个 Word Embedding \(w_i\) 上,然后经过一个 Linear Layer 以保证输入到 PLM Encoder 的维度,最后将其输入到 PLM Encoder 中
BlackImage:为了验证提示向量(Prompt Vectors)是否使用了来自 VE 的视觉信息,我们 使用黑色图像训练提示向量
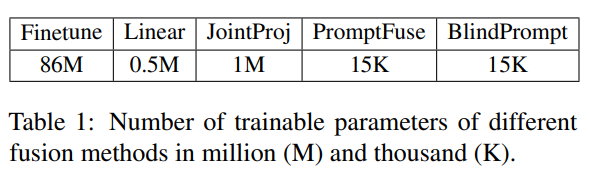
两种模态:Text & Image
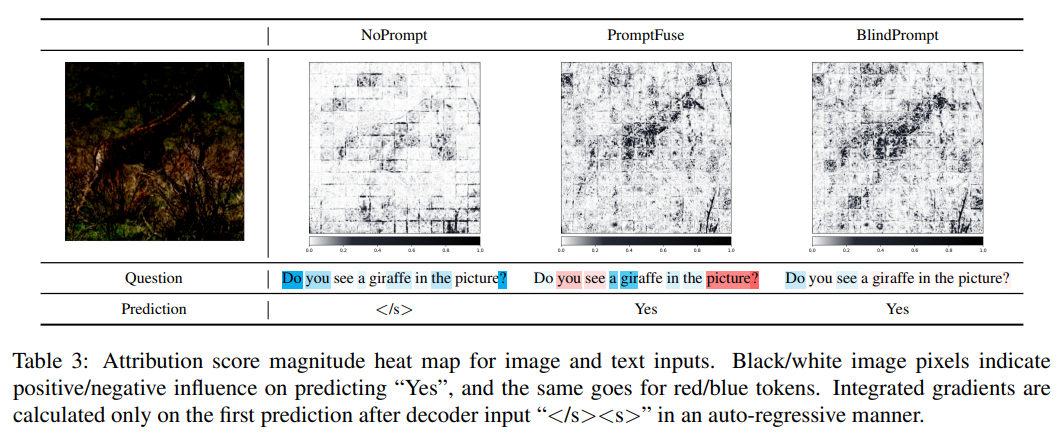
定性例子——使用积分梯度
We apply the Integrated Gradients(积分梯度) method, which measures the attribution of features to the neural network outputs.
In practice, we use the Captum package in our implementation.
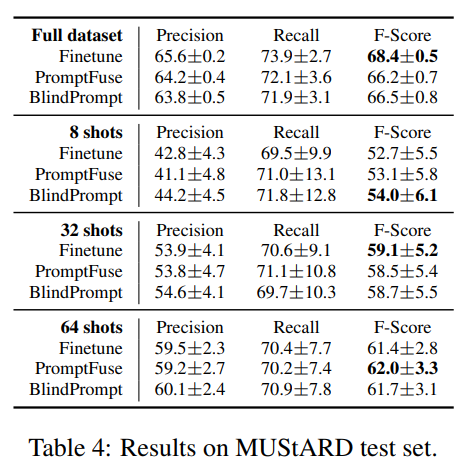
三种模态:Text & Video & Audio
参考
文档信息
- 本文作者:Bookstall
- 本文链接:https://bookstall.github.io/2023/03/16/PromptFuse-and-BlindPrompt/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)